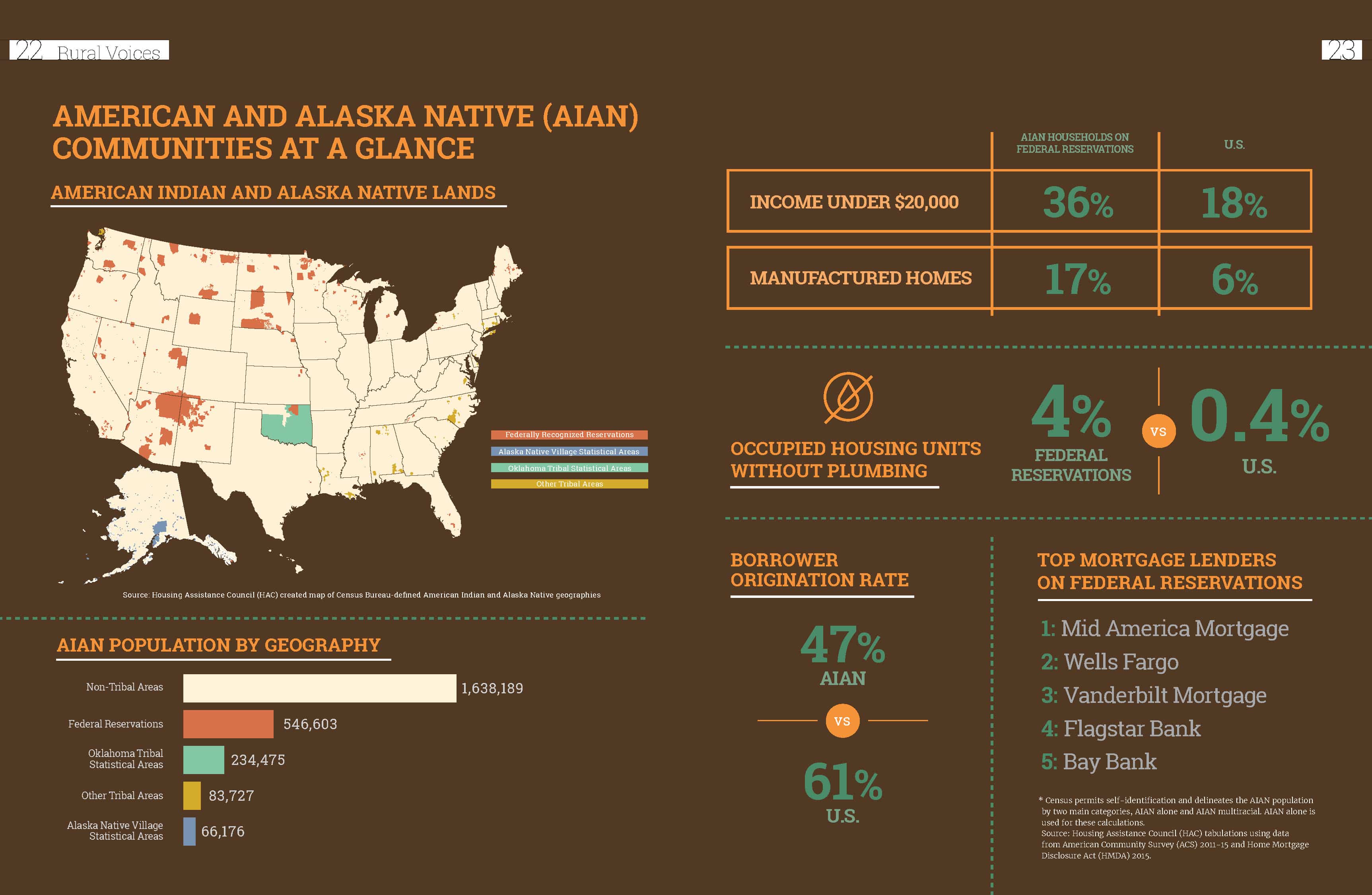
White Mountain Apache Housing Authority Serves its Veterans
The White Mountain Apache Housing Authority (WMAHA) helps the members of the White Mountain Apache Tribe to overcome their individual housing needs. Of these, almost 500 are U.S. military veterans. Working in the Fort Apache Indian Reservation located in eastern central Arizona, WMAHA serves the 16,000 enrolled members of the White Mountain Apache Tribe and strives to ensure that every tribal member has safe housing they can afford. The Housing Assistance Council (HAC) is proud to be a partner of WMAHA and their amazing work. In 2018, we awarded a $30,000 grant through The Home Depot Foundation‘s Veteran Housing Grants Program to WMAHA to help support their veterans. In celebration of Veterans Day and Native American Heritage Month, we’d like to highlight just a few of the many ways the White Mountain Apache Housing Authority serves the veterans of the White Mountain Apache Tribe.
 Before rehab of a veteran’s home completed by WMAHA in 2018 |
 After rehab of a veteran’s home completed by WMAHA in 2018 |
| Before and after of a rehab of a veteran’s home completed by WMAHA in 2018
|
|
As many veterans know, service doesn’t end when you’re discharged. It’s a value that is carried for a lifetime. For WMAHA, service is key to the mission. The Veteran Home Rehabilitation Program serves those who have served our country. Many of the low-income Apache veterans the Housing Authority assists are in desperate need of multiple, expensive repairs to make sure their homes are safe, accessible, and livable. But without the ability to make these repairs themselves, many veterans need help.
Over the last eight years, the White Mountain Apache Housing Authority has rehabilitated (or in one case built!) 19 homes for their veterans, each of which required multiple major repairs for health, safety, and accessibility. All of this was performed at no cost to the veteran or their family. Last year WMAHA was able to set a record with 5 rehabilitations.
Making sure their veterans have safe and healthy homes is a point of pride for WMAHA and for the entire White Mountain Apache community. After all, WMAHA doesn’t work alone: each rehabilitation is made possible by scores of volunteers. As the team from WMAHA explains, “the number of volunteers who come and help with demolition and construction cleanup during the projects” is a testament to the rehabilitation program’s “impact on the community.” From the Housing Authority to everyday members, including community partners, the White Mountain Apache Tribe takes care of its veterans. By taking care of those who took care of us, WMAHA is serving both its community and the broader community of veterans nationwide.
The COVID pandemic has hit many Native communities particularly hard, and tragically, the White Mountain Apache are no exception. During the pandemic, unemployment, which usually runs 80% according to WMAHA, has far surpassed that amount, and food insecurity is “at a critical level.” Many of the low-income veterans WMAHA assists don’t have a way to pick up food from the local food bank, so the Housing Authority is starting to deliver the food boxes itself. Not content to just help house their veterans, WMAHA is committed to improving their quality of life.
Caring for veterans extends outside the home, too. For WMAHA, ensuring their veterans have access to the Veterans Affairs benefits they deserve is a critical mission. With 1.67 million acres, the Fort Apache Indian Reservation is large and rural. This creates challenges for many of the Tribe’s low-income veterans. Many of the nearest VA hospitals are hundreds of miles away, which makes even getting to routine appointments incredibly difficult. This distance makes it so challenging to receive disability ratings, see specialists, and make necessary appointments that, according to Barb Connerley, a consultant who works with WMAHA, “many of the veterans…do not know what VA benefits are available to them.”
 This veteran’s home was in such disrepair the team from WMAHA decided to tear it down and start from scratch. |
 This veteran’s home was in such disrepair the team from WMAHA decided to tear it down and start from scratch. |
| This veteran’s home was in such disrepair the team from WMAHA decided to tear it down and start from scratch. | |
The White Mountain Apache Housing Authority has created a solution to help connect their veterans to the VA medical care they earned through their service. Since 2017, the White Mountain Apache Tribe Department of Transportation has operated Fort Apache Connection Transit (FACT), a 2-route bus system serving 12 stops across the Reservation. While this system doesn’t provide access to the nearest VA hospitals, the Housing Authority recently began repurposing one of their buses to transport veterans to their VA appointments. Multiple times a month, WMAHA will be providing veterans with a bus ride to their appointments and back home. They even take the time to help the veterans complete their paperwork to file for VA benefits.
For the trip, WMAHA provides their veterans with water, snacks, masks, and COVID safety information. They hope that this program can also serve as a teaching event, helping their veterans learn more about COVID safety as well as how to access their VA benefits. The program’s strength is its ingenuity—bringing together transit, healthcare, and informational services—in solving a critical problem for the Tribe’s veterans. Thanks to the White Mountain Apache Housing Authority, veterans living on reservation now have access to the critical VA healthcare they’ve earned through their service.
Many veterans return from their service to find it difficult to access the resources of their communities, including housing. Tragically, Native communities are overrepresented among persistent poverty counties, making these resources even harder to access. The Housing Assistance Council is committed to helping build community resources for housing where they’re needed most. Partners like WMAHA help us give back to our veterans and uplift Native communities. As Barb Connerley puts it, the Tribe’s veterans “have a proud tradition of military service and sacrifice.” The work of the White Mountain Apache Housing Authority pays respect to that service and sacrifice through service, care, and ingenuity of its own.











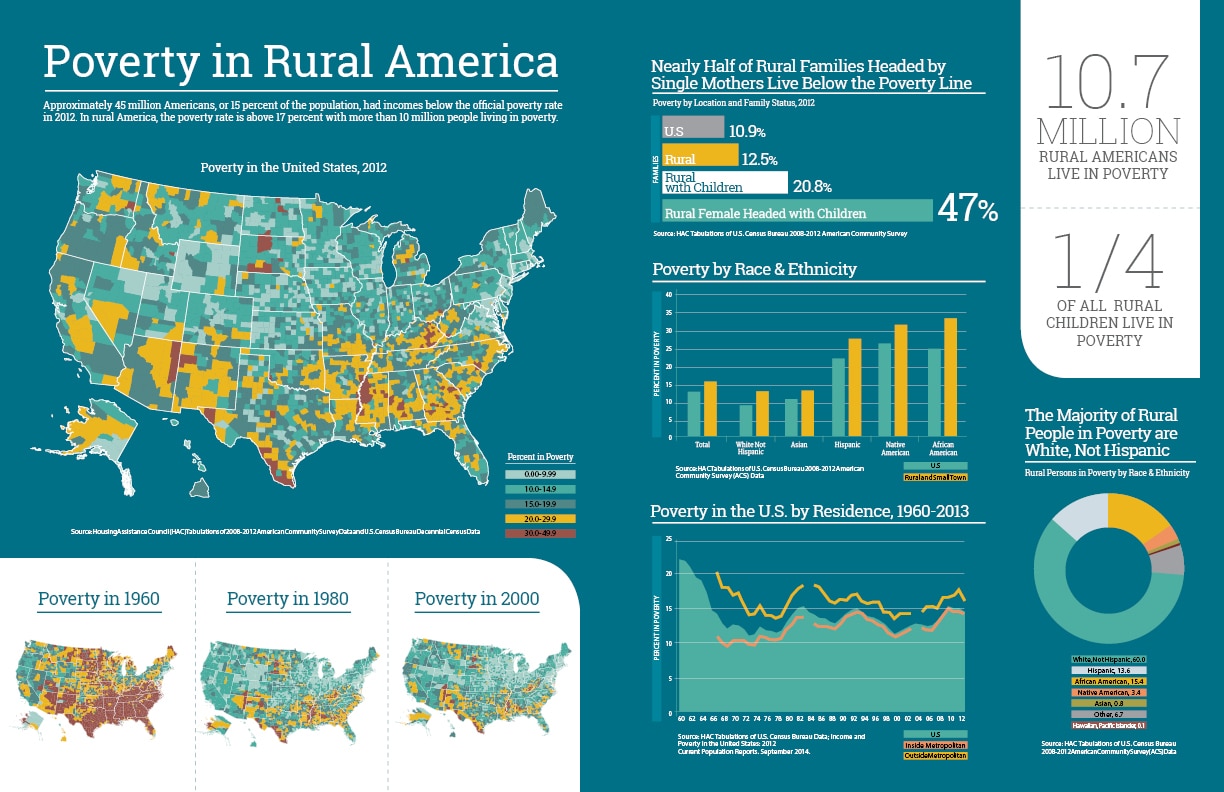 Poverty in Rural America
Poverty in Rural America

