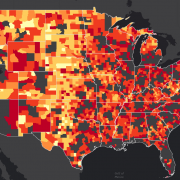
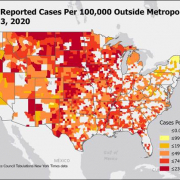
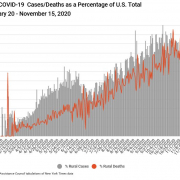
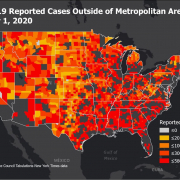
Middle Tennessee Flooding Disaster Guide
On August 21, 2021, record-breaking rain (17 inches in 24 hours) caused major flooding in Middle Tennessee and at least 22 fatalities in Humphreys County. Roads, telephone lines, cars, and home foundations were washed away. HAC offers the following guide as a source of information for individuals and families dealing with direct housing loss and damage from the storm. For more information, please see HAC’s report: Picking up the Pieces: Restoring Rural Housing and Communities After a Disaster and Disaster Response for Rural Communities Guide.
If your house is inaccessible or currently uninhabitable, emergency, transient housing will likely be made available to provide immediate shelter for those in need. Organizations and resources available to assist with emergency transient housing in previous similar disasters include the Red Cross, Salvation Army, Church World Service, Mennonite Disaster Service, and state- and city-run emergency shelters. If you are in need of emergency, transient housing, you can text SHELTER and your Zip Code to 43362 (4FEMA) to find where the shelter closest to you is located.
FEMA makes available temporary assistance funding available for residents of counties affected by natural disasters. Temporary assistance can include grants for temporary housing and home repairs, low-cost loans to cover uninsured property losses, and other programs to help individuals and business owners recover from the effects of the disaster. To see if you are eligible for funding, you can apply online at https://www.disasterassistance.gov/ or call FEMA’s toll-free helpline at 1-800-621-FEMA(3362). When applying, make sure to have a pen and paper as well as the following information: your social security number, current and pre-disaster address, a telephone number where you can be contacted, insurance information, total household income, a routing and account number from your bank if you are interested in having disaster assistance funds transferred directly into your bank account, and a description of your losses that were caused by the disaster.
Tips
Please keep in mind the following safety protocols for flooding:
- Only call 911 if you have an immediate need for medical attention or evacuation assistance.
- If you can’t get through to 911 on first try, keep calling.
- DO NOT DRIVE through high water and DO NOT DRIVE AROUND BARRICADES! Just 2 feet of water can sweep your vehicle away.
- DO NOT WALK through flood waters. Just 6 inches of moving water can knock you down. 4
- If your home floods, STAY THERE. You are safer at home than trying to navigate flooded streets on foot.
- If floodwaters rise around your car but the water is NOT MOVING, abandon the car and move to higher ground. Do not leave the car and enter MOVING water.
- STAY AWAY from streams, rivers, and creeks during heavy rainfall. These areas can flood quickly and with little warning.
- MOVE important items – especially important documents like insurance policies – to the highest possible floor. This will help protect them from flood damage.
- DISCONNECT electrical appliances and do not touch electrical equipment if you are wet or standing in water. You could be electrocuted.
This flooding event is a reminder that all residents in this area should carry flood insurance. Contact your insurance agent for more information about purchasing flood insurance or visit the National Flood Insurance Program at www.fema.gov/national-flood-insurance-program or call 1-888-379-9531. Please keep in mind that new insurance policies take 30 days to go into effect.
If your home has experienced damage, remember to check the outside of your home before you enter. Look for loose power lines, broken or damaged gas lines, foundations cracks, missing support beams, or other damage. It may be safest to ask a building inspector of contractor to check the structure before you enter. Do not force jammed doors open, as they may be providing needed support to the rest of the home. Sniff for gas to ensure there are no natural or propane gas leaks. If you do have a propane tank system, make sure to turn off all valves and contact a propane supplier to check the system before you use it again. Check floors and ceilings to ensure they are not sagging from water damage. This can be especially hazardous. Take photographs of any damage as you may need them for insurance claims or FEMA claims later on.
Resources
Apply for FEMA Assistance by registering online at www.DisasterAssistance.gov. FEMA Disaster Assistance Helpline answers questions about the help offered by FEMA, how to apply for assistance, or the information in your account.
Toll-free helpline: 1-800-621-FEMA (3362)
For hearing impaired callers only:
1-800-462-7585 (TTY)
1-800-621-3362 (Video Relay Service)
Operators are multilingual and calls are answered seven days a week from 7 a.m. to 11 p.m. ET
American Red Cross Disaster Service: For referrals and updates on Red Cross shelter services in your area, locate a local Red Cross office through: https://www.redcross.org/find-help or by calling 1-800-RED CROSS (1-800-733-2767)
The Red Cross helps disaster victims by providing safe shelter, hot meals, essential relief supplies, emotional support and health services like first aid. Trained Red Cross workers often meet one-on-one with families to develop individual plans and identify available resources to help aid recovery.
STATE HOUSING AGENCIES
Tennessee
Tennessee Housing Development Agency
502 Deaderick Street, Third Floor
Nashville, TN 37243
Phone: (615) 815-2200
Fax: (615) 564-2700
https://www.thda.org
DEPARTMENT OF HOUSING AND URBAN DEVELOPMENT STATE FIELD OFFICES
Tennessee
John J. Duncan Federal Building
710 Locust Street, SW 3rd Floor
Knoxville, TN 37902-2526
Phone: (865) 545-4370
Nashville Field Office
235 Cumberland Bend
Suite 200
Nashville, TN 37228-1803
Phone: (615) 515-8510
Director: Sernorma L. Mitchell
USDA RURAL DEVELOPMENT STATE OFFICES
Tennessee
Jim Tracy, State Director
441 Donelson Pike, Suite 310
Nashville, TN 37214
Voice: (615) 783-1300
Fax: (855) 776-7057
www.rd.usda.gov/tn
STATE EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCIES
Region 4 (Mississippi and Tennessee)
Federal Emergency Management Agency
3003 Chamblee Tucker Road
Atlanta, GA 30341
Main Number: 770-220-5200
Fax Number: 770-220-5230


 Housing Assistance Council
Housing Assistance Council Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies
Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies