Covid-19 Cases Surpass 900,000 In Rural America – 20,000 Deaths
Coronavirus cases in rural America are as high as they have been since the pandemic began. The level of reported rural cases and deaths from the virus now consistently outpace the rural share of the national population.
UPDATE: Covid-19 in Rural America
The COVID-19 pandemic is a global health crisis affecting nearly every community – including rural America. While there are still many uncertainties, the health crisis changes daily and the pandemic’s impact on rural communities continues to grow and evolve. The Housing Assistance Council (HAC) presents summary findings of COVID-19 in rural America as of early October 2020.
MORE THAN 900,000 RURAL AMERICANS HAVE BEEN INFECTED WITH COVID-19
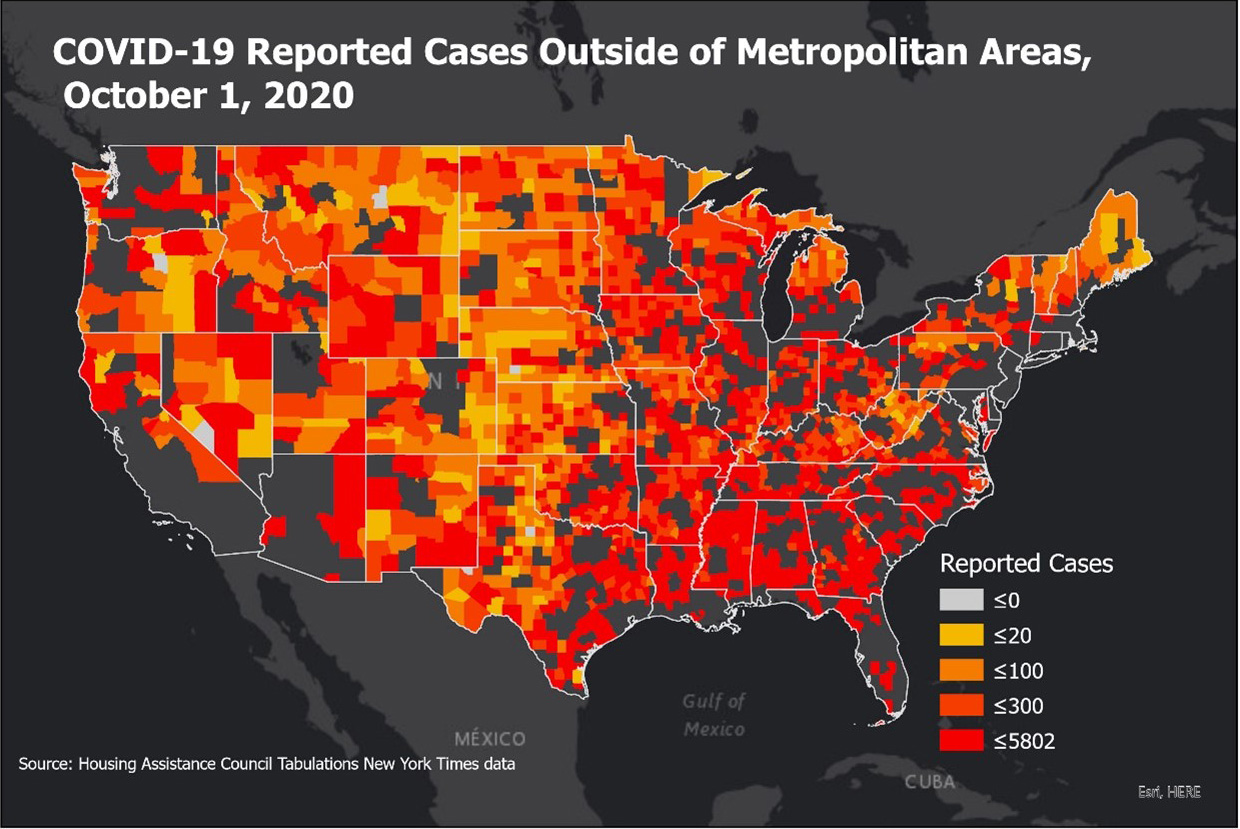
Total Reported COVID-19 Cases February 20- October 1, 2020
The first reported case of COVID-19 outside of metropolitan areas came on February 20, 2020. As of October 1, 2020, there were more than 900,000 reported cases of COVID-19 and approximately 20,000 associated deaths in communities outside of metropolitan areas. All but 9 counties outside of metropolitan areas now have reported COVID-19 cases, and nearly 80 percent of outside metro counties have also reported associated deaths related to the virus.
RURAL CASES ARE AT THEIR HIGHEST LEVELS SINCE THE PANDEMIC BEGAN
Rural Share of COVID-19 Reported Cases
Nationally, the number of new COVID-19 cases have begun to increase again and reported rural cases have also grown to some of their highest levels since the pandemic began. Between September 17 and October 1, rural areas reported an average of 8,543 cases per day – an upward trend of about 25 percent in the past 14-day period. Similarly, rural reported COVID related deaths were up 17 percent over the past 14 days.
RURAL COVID CASES NOW OUTPACE THE OUTSIDE METROPOLITAN POPULATION AS A WHOLE
Rural Share of COVID-19 Reported Cases
Initial impacts of COVID-19 were greatest in urban communities and these areas still have the largest share of cases and deaths. Since February 20, 2020, about 12 percent of the total reported COVID-19 cases were identified in rural communities. But the rural share of COVID-19 cases continues to rise nationally. On September 1, 2020, approximately 15 percent of new COVID-19 cases and 19 percent of deaths were reported in rural communities. On October 1, 2020, 22 percent of new cases and 23 percent of new deaths were reported outside of metropolitan areas.
RURAL COVID-19 CASES ARE HIGHEST IN THE SOUTH AND INCREASING IN THE UPPER MIDWEST
Reported Rural COVID-19 Rates per 100,000
Over 99 percent of counties outside of Metropolitan areas have reported COVID-19 cases, but the virus’ impacts vary widely across the nation’s rural geography. There have been several instances of extremely high per-capita infection rates in rural areas – notably on some Native American lands and communities with meat packing and correctional facilities. From September 1- October 1, the rural case and death rates increased most dramatically in the plains and upper Midwest, as well as in some Appalachian and southern communities.
ABOUT THE DATA
The information in this brief derives from Housing Assistance Council tabulations of data from The New York Times, based on reports from state and local health agencies, and the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2014-2018 American Community Survey.
In these analyses, the terms “rural” and Outside Metropolitan Areas are synonymous and refer to counties and counts outside of OMB designated Metropolitan Areas.
The Housing Assistance Council is a national nonprofit organization that helps build homes and communities across rural America.