Building homes together in America’s “most rural state”
As part of National Homeownership Month, we’ll be highlighting stories from across our network participating in the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development’s (HUD) Self-Help Homeownership Opportunity Program (SHOP). HAC provides loan funds to self-help housing providers to help low- and moderate-income families achieve their dreams of homeownership. The homebuyer family must contribute a significant amount of sweat-equity towards the construction of the dwelling. Loan funds are awarded through a competitive application process. If the organization meets certain requirements, up to 90% of the SHOP loan may be forgiven. The forgivable portion may become a grant for the group to establish its own revolving loan fund for future site acquisition and development of self-help housing or to provide direct subsidies to participating homebuyer families.

Community Concepts staff and supporters celebrate the completion of news self-help units in 2019
Following the 2010 Census, Maine was dubbed “the most rural state” with 61.3% of its residents living in rural communities. Homeownership is common among Mainers, with 71.5% of all units being owner-occupied. Though poverty rates in Maine are lower than the national average (13.5% vs. 15.1%), the state has higher rates of residents receiving income through Social Security, Supplemental Social Security, and Public Assistance making it challenging for many to qualify for a mortgage.
Community Concepts, Inc., based in Lewiston, Maine, got its start in 1965 as part of federal legislation that created a network of Community Action Agencies. Community Concept’s programming focuses on the “whole family”, addressing the needs of parents and their children with programs like Head Start, fuel assistance, weatherization programs, and self-help homeownership. In 1991, HAC provided a planning grant to Community Concepts to help initiate the self-help homeownership program at the organization. “Since that first grant, we’ve completed 350 self-help home ownership opportunity, including new construction and a purchase/repair program we added 10 years ago,” shared Sandy Albert, Director of Housing Improvement Services.
The organization sees a lot of overlap in the clients it serves and that is intentional. “We have family development coaches that are working with families,” says Albert. If a family of renters comes to the agency looking for help with fuel assistance the coach will also ask if they’re interested in becoming a homeowner. The coach will then refer the family to other programs in the organization that can help them pursue homeownership or, if necessary, help build their credit.
One of those families, the Hoyts, achieved their dream in May 2012. Working together with five other families, the Hoyts learned valuable construction skills as they worked on their home. Through their sweat-equity, each family saved as much as $20,000 on the cost of their home. In a letter shared by Community Concepts, Eric Hoyt wrote “This is not a house that you’re building it’s a home, and it’s a heartfelt build. With a lot of meaning that goes into it. There is a lot of hours and tears and fears but through them all when you walk through the door and you say look at what we have. When you look at what you and your team has accomplished it makes it that much more a home.”
Albert credits the program’s success and impact to Community Concept’s partnership with HAC. “Without the funding through SHOP, many of our buyers would not qualify even with the sweat-equity,” said Albert “those families wouldn’t be where they are today.”







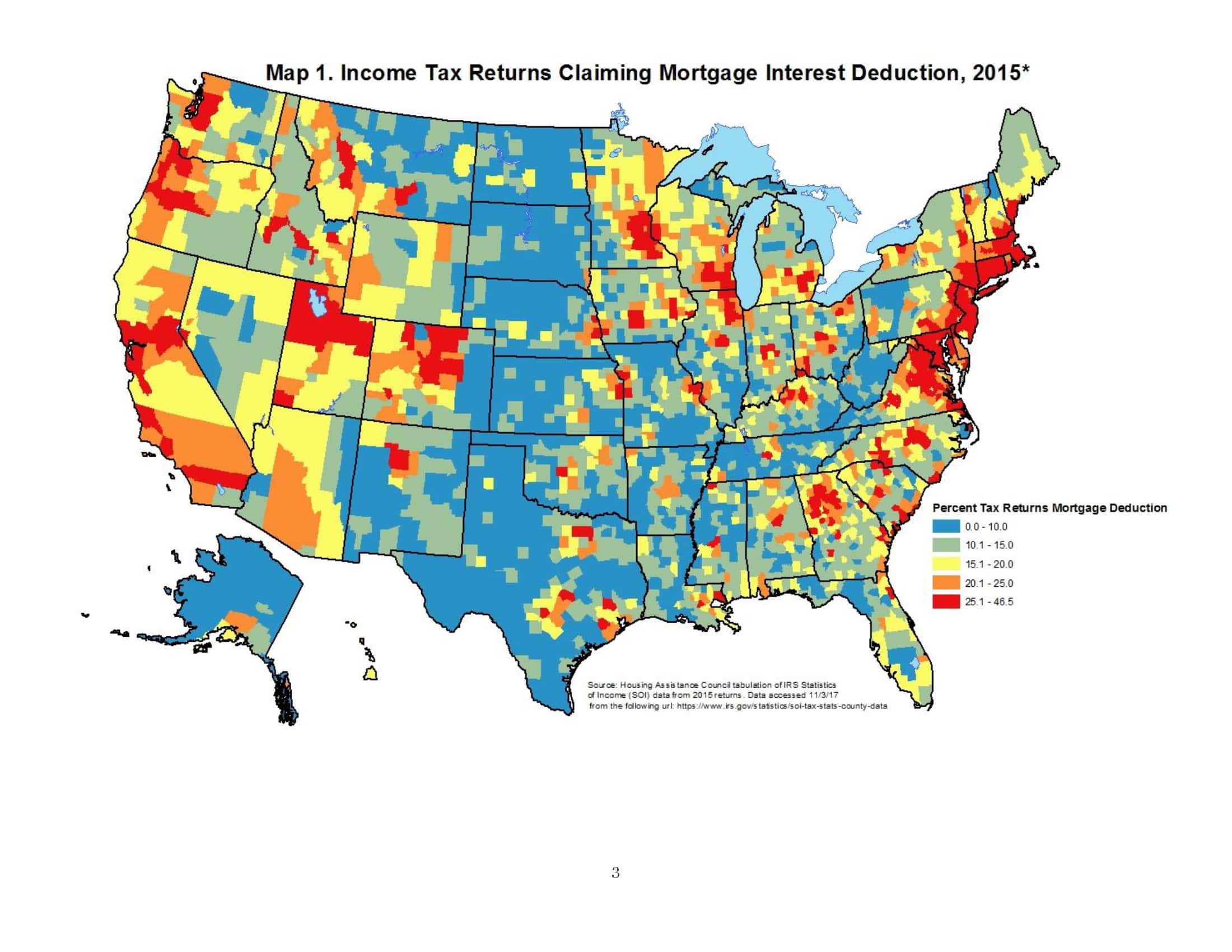






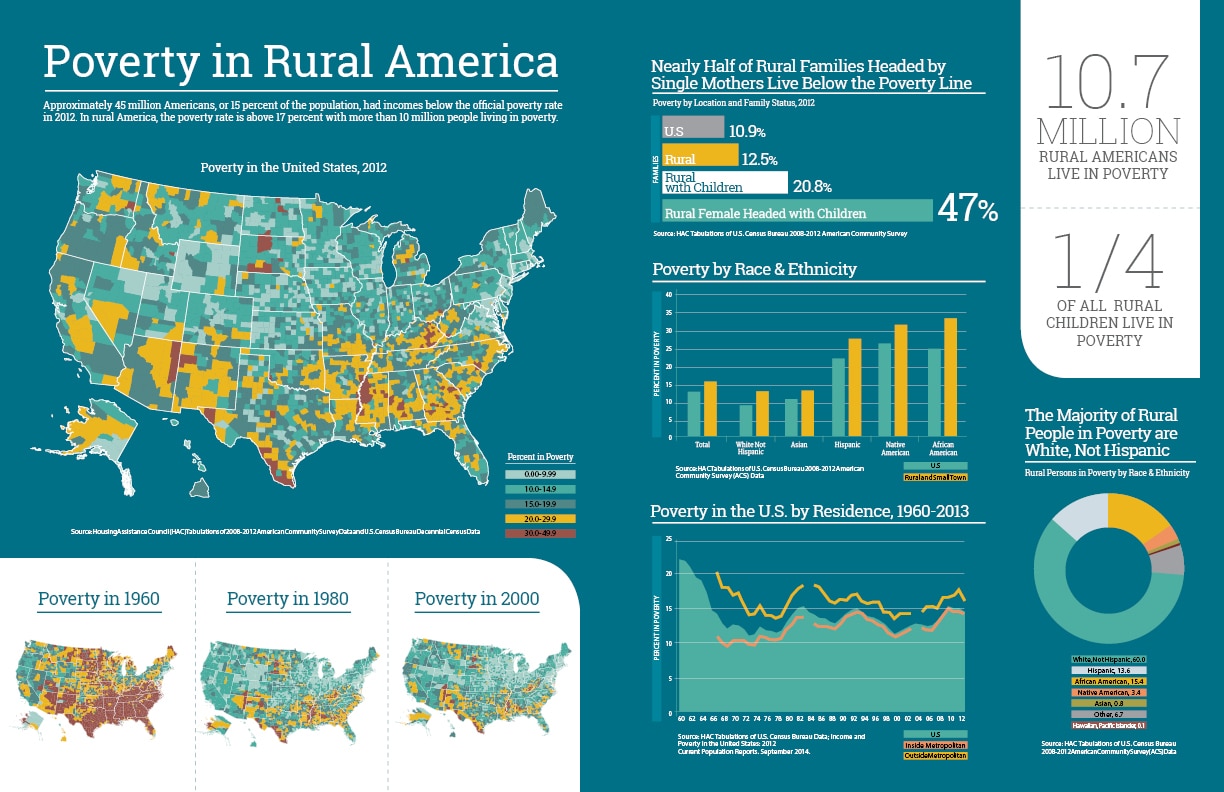 Poverty in Rural America
Poverty in Rural America
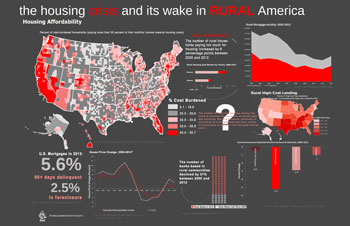 The housing crisis and its wake in rural America
The housing crisis and its wake in rural America
